Heritage Rice: Unlocking Nature’s Antiviral Potential Against SARS-CoV-2
Identifying the Issue
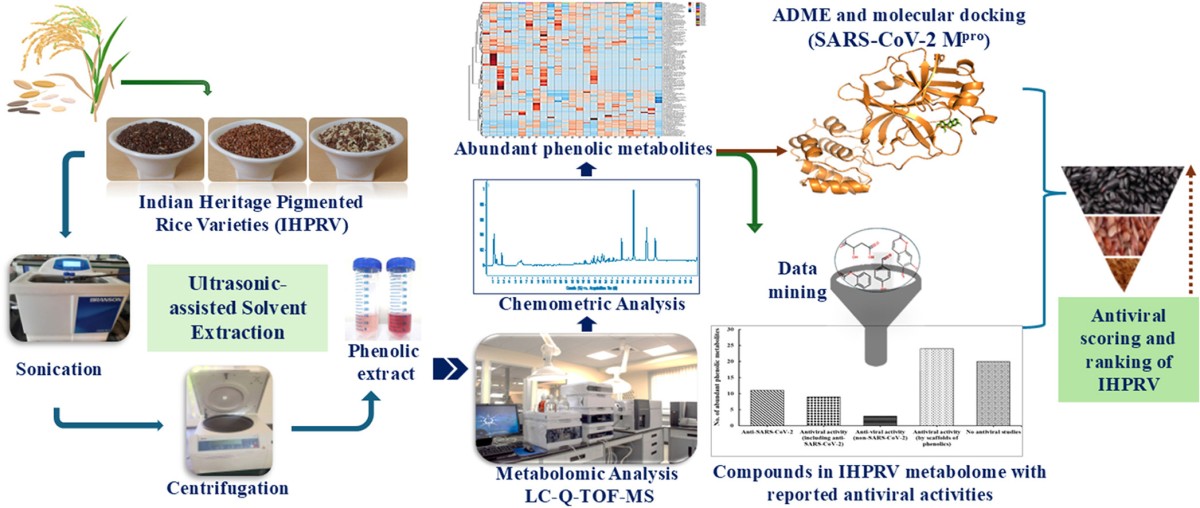
- Need to explore a diverse range of bioactive polyphenols in underexplored Indian heritage pigmented rice varieties (IHPRV)
- Lack of studies on antiviral activities of pigmented rice polyphenols
Objective of the Research
- To thoroughly screen phenolic metabolites in IHPRV through LC-Q-TOF-MS-based metabolomic profiling
- To conduct exhaustive data mining through literature and database screening of identified abundant phenolic metabolites for their antiviral activities with a special focus on anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity
- To investigate the anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of phenolic compounds lacking studies on their antiviral potency through in silico analysis
- To score and rank IHPRV with the maximum number of antiviral polyphenols present in them based on results obtained from data mining and molecular docking analysis
Who should read this?
Research scientists, food scientists, nutritionists, dieticians, pharmaceutical scientists and inventors, health food industries
Solution
- LC-Q-TOF-MS-based metabolomic profiling is a high-end analytical technique for screening unexplored polyphenols present in the experimental samples
- Data screening provides an understanding of the compounds not explored for their antiviral properties
- In silico analysis serves as an effective approach to assess the antiviral properties of abundant polyphenols prior to validation in an in vitro setting
Key Features and Benefits
- Metabolomic analysis revealed 132 diverse polyphenols, with flavonoids (predominantly anthocyanins and flavones) as the major category in 24 IHPRV, of which 67 were abundant
- Data mining helped identify over 45 compounds/their scaffolds from the pigmented rice metabolome to exhibit antiviral activity
- Molecular docking analysis revealed five additional polyphenols in the IHPRV metabolome with anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity (≤ -7 kcal/mol binding energy value)
- A systematic ranking of IHPRVs for their antiviral potency based on results obtained from data mining and molecular docking analysis revealed Karupa Kavuni (BKk), a black rice variety, to be the lead sample among the 24 varieties
Impact
- Identification of antiviral pharmacological activities of various bioactive compounds in IHPRV provides a strong basis for developing nutraceuticals for viral defense
- Nutritionists and the health food industry can work in collaboration to use these lead IHPRV for formulating antiviral functional food products
- Aims to foster collaborations between food scientists, nutritionists, and healthcare providers to ensure that the product is effective, safe, and well-integrated into dietary recommendations
- Inclusion of top-ranked IHPRV as a functional food or as a dietary supplement is a safe and economical option
Team
Shrijana Rasaily, Ashrita C. Haldipur and Prof. N. Srividya, Department of Food and Nutritional Sciences, Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning.
Title of paper: “LC-Q-TOF-MS phenolic profiling, data mining for antiviral compounds, and in silico analysis against SARS-CoV-2 in heritage-pigmented rice metabolome”
Read Paper Here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2024.105613